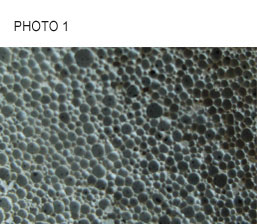
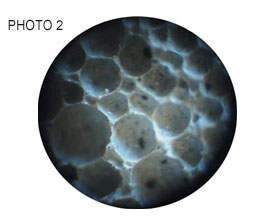
Cellular concrete is a material which consists of a solid cement matrix that contains lots of small air bubbles in its interior. The particles of solid material are bonded to each other by a large adhesive effect that produces a deformation on the sphere, in the contact surface between them. When a cross- sectional section of the material is observed using a magnifying lens (photos 1 and 2), a similar appearance to a bees honeycomb can be seen. This arrangement reduces cement consumption to a minimum amount of wax.
The unit forms a three- dimensional reticular structure. This structural geometry contributes to the high compressive strength of C.C.
 |
|
 |
| Photo 1. Cut section of technical cellular concrete sample (CC 250). Photograph at 5 times magnification. |
|
Photo 2. View of sample CC 250. Photograph at 30 times magnification. View of the complete bubble. |
 |
|
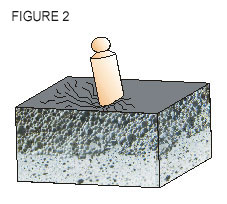 |
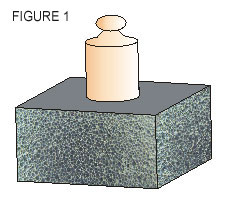
Figure 1. Graphical representation of the behavior of a technical C.C. Excellent compressive strength, low cement cost. Air occlusion in uniform bubbles and with reticular structure of homogeneous geometry through out the whole section. Excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties. |
|
Figure 2. Graphical representation of the behavior of a poor quality CC. Mixing with inadequate machinery and a chemical additive of poor tensioactive properties causes precarious compressive strength, with a fragile superficial layer, air occlusions in bubbles which are broken forming a cement conglomerate with large holes. Heterogeneous section and with high cement cost. No insulation properties. |
|